UNCLOS defines zones of coastal jurisdiction, including inland waters, territorial sea, archipelagic water, contiguous zone, continental shelf, and EEZ. No country can claim any zone as per their wish, it has to be as per UNCLOS.
The main objectives of UNCLOS are:
- Facilitation of international communication,
- Promotion of peaceful uses of the sea and oceans,
- Equitable and efficient utilization of the sea and oceans,
- Protection and preservation of the marine environment,
- Promoting maritime safety.
Principles of UNCLOS
- Freedom of high seas,
- Peaceful uses of world oceans,
- National sovereign over territorial waters,
- Freedom of innocent passage of the ships through territorial waters and archipelagic zones,
- Freedom of transit through international straits,
- Marine environment protection,
- Peaceful settlement of a dispute.
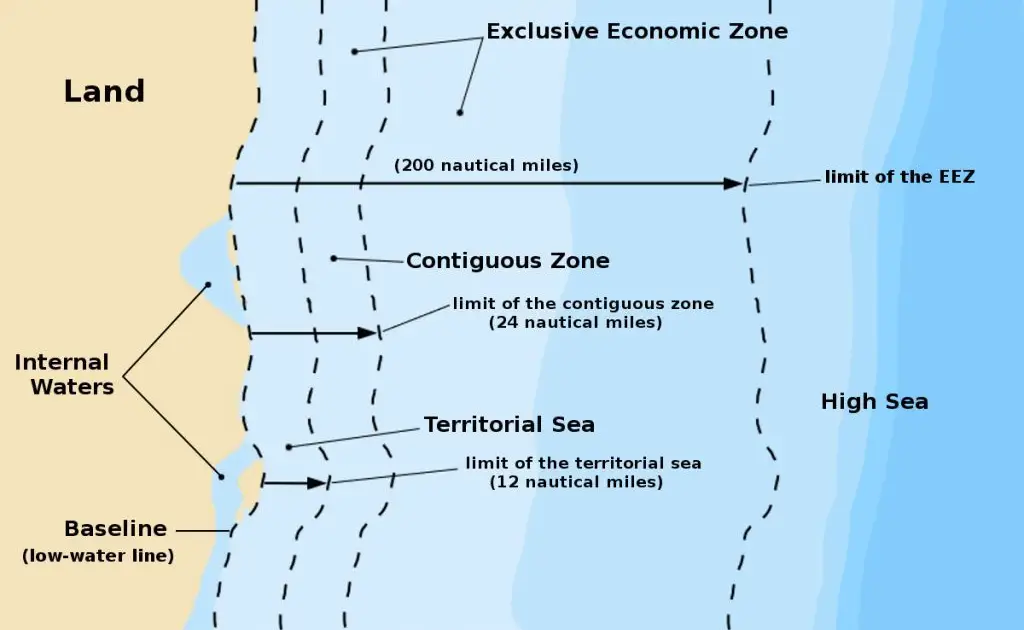
Normal baseline: it is the low water line along the coast as marked on the large scale chart officially recognized by the coastal state.
Inland waters: this extends from the shore to the baseline. Within this zone, the coastal state has jurisdiction and sovereignty in the same manner as it has over its land. Foreign vessels have the right of innocent passage through inland waters only in case of distress. While foreign vessels are subject to the jurisdiction, the coastal state does not enforce their laws on the vessels except:
- When an offense of the vessel affects peace and good order of the port,
- When the master of the vessel requests the coastal state to exercise jurisdiction,
- When a person other than a crew member is involved,
- When the vessel breaches local regulations on pollution, navigation, custom and immigration regulations, security, etc.
For example: if a crime is committed on a foreign vessel in port it is perfectly within the rights of the coastal state to investigate the matter, however, it is up to the coastal state to exercise it or leave the matter to the flag state of the vessel.
The territorial sea extends up to a distance of 12 nm seaward of the baseline. Within this zone, the coastal state has jurisdiction and sovereignty in the same manner as it has over its land.
One difference between i.w. And t.s. Is that jurisdiction does not extend to criminal matters except:
- When consequences of the crime extend to the coastal state.
- Disturbs peace and good order,
- To suppress illicit traffic of narcotic drug,
- Master of v/l requests.
Foreign vessels have the right of innocent passage through t.s.
Contiguous zone: it extends seaward from the baseline up to 24nm. Over this, the coastal state does not exercise sovereignty but only 4-fold jurisdiction with regards to customs, fiscal, immigration, and sanitary matters.
Exclusive economic zone: this is an area beyond and adjacent to territorial sea over which the coastal state will have sovereign rights and exclusive jurisdiction for the purpose of exploration and exploitation of natural resources, both living and non-living, production of energy from water, current, and winds, scientific research, etc.
The width of this area is not to exceed more than 200nm from the baseline from where territorial seas are measured.
Duties of flag state
States are obliged to maintain a register of ships under its flag and set up procedures for control of safety, manning, training of crews, pollution aspects, prevention of collisions, etc aspects of ship operation. The flag state has complete jurisdiction over the ship when on high seas.
The nationality of ships:
- Every ship shall fix the conditions for the grant of its nationality to ships, for the registration of ships in its territory, and for the right to fly its flag.
- Every state shall issue to the ships to which it has granted the right to fly its flag documents to this effect.
Exercise the jurisdiction and control of administrative, technical, and social matters
Every State shall effectively exercise its jurisdiction and control in administrative, technical, and social matters over ships flying its flag.
In particular, every state shall:
- Maintain a register of ships containing the names and particulars of ships flying its flag.
- Assume jurisdiction under its internal law over each ship flying its flag and its master, officers, and crew in respect of administrative, technical, and social matters concerning the ship,
- Every ship shall take measures for ships flying its flag as are necessary to ensure safety at sea with regard to:
- The construction, equipment, and seaworthiness of ships,
- The manning of ships, labour condition and the training of crews,
- The use of signals, maintenance of communications, and the prevention of collision.
- Each ship, before registration and thereafter, is surveyed, by a qualified surveyor of ships and has on board such charts, nautical publications, and navigational equipment and instruments as are appropriate.
- Each ship is in the charge of a master, officers, engineers who possess the necessary knowledge, qualification, and certification.
- Each ship is adequately manned.
Piracy as per UNCLOS
Piracy consists of any of the following:
- Any illegal acts of violence or detention, or any act of depredation, committed for private ends by the crew or the passengers of a private ship or a private aircraft, and directed:
- On the high seas, against another ship or aircraft, or against persons or property on board such ship or aircraft,
- Against a ship, aircraft, persons, or property in a place outside the jurisdiction of any state,
- Any act of voluntary participation in the operation of a ship or of an aircraft with knowledge of facts making it a pirate ship or aircraft,
- Any act of initiating or of intentionally facilitating an act as described above.
Freedom of high seas
High seas represent that sea area which is not a part of any sovereign state. The high seas are open to all states, whether coastal or landlocked. This is called freedom of high seas, which consists of the following:
- Freedom of navigation,
- Freedom of overflight,
- Freedom to lay submarine cables and pipelines,
- Freedom to construct artificial islands and other installations,
- Freedom of fishing,
- Freedom of scientific research.
Right of innocent passage
Passage means navigation through the territorial sea for the purpose of
- Traversing the sea without entering internal waters or calling a port facility outside internal waters.
- Proceeding to and from internal waters ar a call at such port facility.
- Passage shall be continuous and expeditious. Anchoring and stopping only if incidental, or by force or distress or for the purpose of rendering assistance to persons in distress, is included in the passage.
Meaning of innocent passage
A passage is innocent so long as it is not prejudicial to the peace, good order, or security of the state. Passage of a ship shall not be considered innocent if she is engaged in any of the following activities:
- threat or use of force against the sovereign state.
- exercise or practice with weapons of any kind.
- Any act of collecting information relating to the defense and security of the state
- The launching, landing, or taking on the board of any aircraft.
- The launching, landing, or taking in of any military device.
- By an act of willful and serious pollution,
- Any fishing activity,
- The carrying out of research or survey activity,
- Any other act not having a direct bearing on passage.
Right of unimpeded transit passage
It means transit through international states. A vessel can perform the following activities:
- Air traffic is allowed,
- Submarine allowed in submerged mode,
- The air carrier can fly and recover aircraft,
- International straits with overlapping territorial seas are examples of unimpeded transit passage.
Seizure of pirate ship
On high seas, or in any other place outside the jurisdiction of any state, every State may seize a pirate ship, or a ship taken by piracy and under the control of pirates, and arrest the persons and seize the property on board. The courts of the state which carried out the seizure may decide upon the penalties to be imposed, and also determine the action to be taken with regard to the ships or property, subject to the rights of third parties acting in good faith. When a ship seized on suspicion of piracy without adequate grounds, the state making the seizure shall be liable for any loss or damage caused by the seizure.
Right of hot pursuit
- The hot pursuit of a foreign ship may be undertaken when the competent authorities of the coastal state have a good reason to believe that the ship has violated the laws and regulations of that state.
- Such pursuit must be commenced when the foreign vessel or one of its boats is within the internal waters, territorial sea, or the contiguous zone of the pursuing state.
- A right of hot pursuit shall apply to violations in the EEZ or continental shelf, including safety zones around the continental shelf installations or of the laws and regulations of the coastal state.
- The right of hot pursuit ceases as soon as the ship being pursued enters the territorial waters of her own state or any other state.
- The right of hot pursuit may only be exercised by warships or military ships or any other ship clearly marked and identifiable as a ship on government service.
- Where a ship has been stopped or arrested outside the territorial sea in circumstances which do not justify the exercise of right oh hot pursuit, it shall be compensated for any loss or damage it might have sustained as a result of such stoppage or arrest.